Top 10 Insights into the Textile Dyeing Process You Need to Know
The textile dyeing process is a pivotal aspect of the textile industry, responsible for transforming raw fabrics into vibrant and appealing finished products. According to a report by the World Bank, textile dyeing accounts for 20% of global industrial water pollution, highlighting the critical need for sustainable practices. As the demand for colorful textiles continues to rise—projected to reach a market value of over $200 billion by 2025—understanding the intricacies of the dyeing process becomes increasingly important for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Moreover, the textile dyeing process involves various techniques, each with its own environmental impact and efficiency levels. Data from the International Textile Manufacturers Federation indicates that up to 15% of the weight of dyed fabric can be lost during various stages of processing due to inefficiencies and wastage. As the industry faces growing scrutiny over its environmental footprint, innovations such as digital printing and eco-friendly dyes are being explored to enhance sustainability while meeting consumer demands. This article aims to highlight the top 10 insights into the textile dyeing process, shedding light on its challenges, advancements, and essential considerations for industry stakeholders.
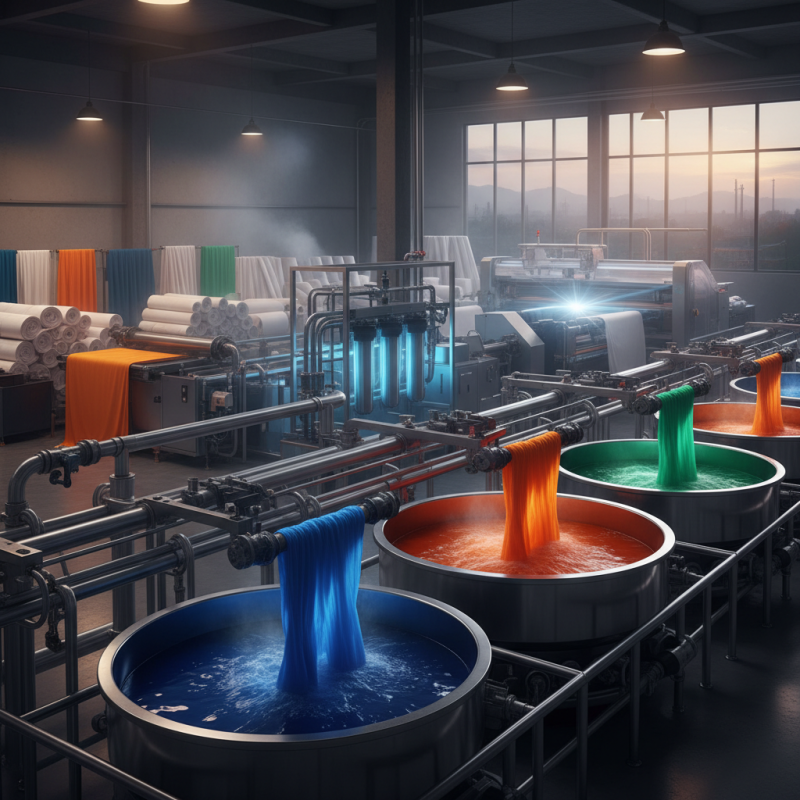

Overview of the Textile Dyeing Process and Its Importance
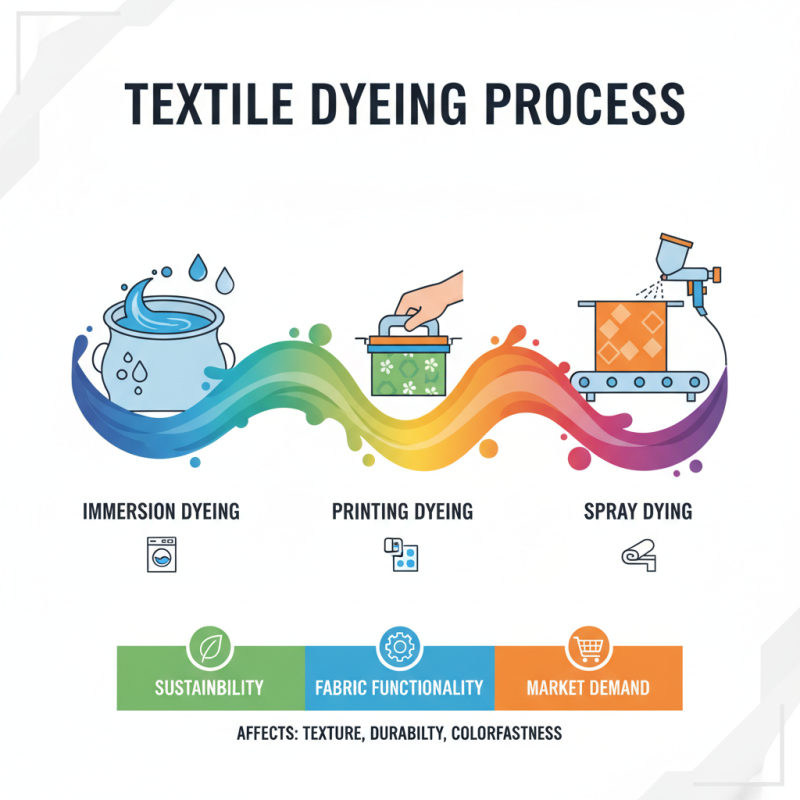
The textile dyeing process is a crucial stage in garment production, significantly influencing the final aesthetic appeal of fabrics. This process involves applying color to textiles through various techniques, including immersion, printing, and spray dyeing. Understanding the significance of dyeing extends beyond visual elements; it encompasses sustainability, fabric functionality, and market demand. Each method contributes distinct characteristics to the material, affecting texture, durability, and colorfastness.
When embarking on the dyeing journey, it’s essential to consider a few tips. First, always conduct small-scale tests before proceeding with large batches to ensure the desired outcome and to avoid waste. Additionally, explore eco-friendly dye options that reduce environmental impact. This not only supports sustainable practices but also appeals to an increasingly conscious consumer base. Finally, keeping abreast of innovative dyeing technologies can enhance efficiency and creativity within your textile projects.
Moreover, effective dye management is vital for optimizing color consistency. Establishing a solid dye recipe and adhering to precise measurements will prevent discrepancies in color during production runs. By prioritizing these aspects, you can ensure high-quality results that resonate in the competitive textile market, leveraging the dyeing process as an asset rather than a merely functional step.
Types of Dyes Used in Textile Dyeing and Their Characteristics
In the textile dyeing process, the choice of dye significantly impacts the final product's colorfastness, appearance, and overall quality. There are various types of dyes utilized in the industry, each with unique characteristics tailored for specific fabrics and dyeing methods.
One of the most common types of dyes is reactive dyes, which form a covalent bond with the fiber, resulting in excellent colorfastness and vibrancy. These dyes are primarily used for cellulose fibers, such as cotton and linen. Another popular category is acid dyes, which are primarily used on protein fibers like wool and silk. These dyes require an acidic environment to fix the color, allowing for rich and intense shades often preferred in high-end textiles.
Furthermore, disperse dyes are favored for synthetic fibers, particularly polyester. They are applied in a disperse form, which allows them to penetrate the fabric during dyeing, producing bright and long-lasting colors. Other notable mentions include direct dyes, which can be applied directly to cellulose fibers with minimal processing, and vat dyes, renowned for their exceptional light and wash fastness, yet requiring complex application processes. Understanding the distinct characteristics of these dye types is essential for achieving desired results in textile dyeing.
Top 10 Insights into the Textile Dyeing Process
Key Factors Influencing the Dyeing Process and Color Fastness
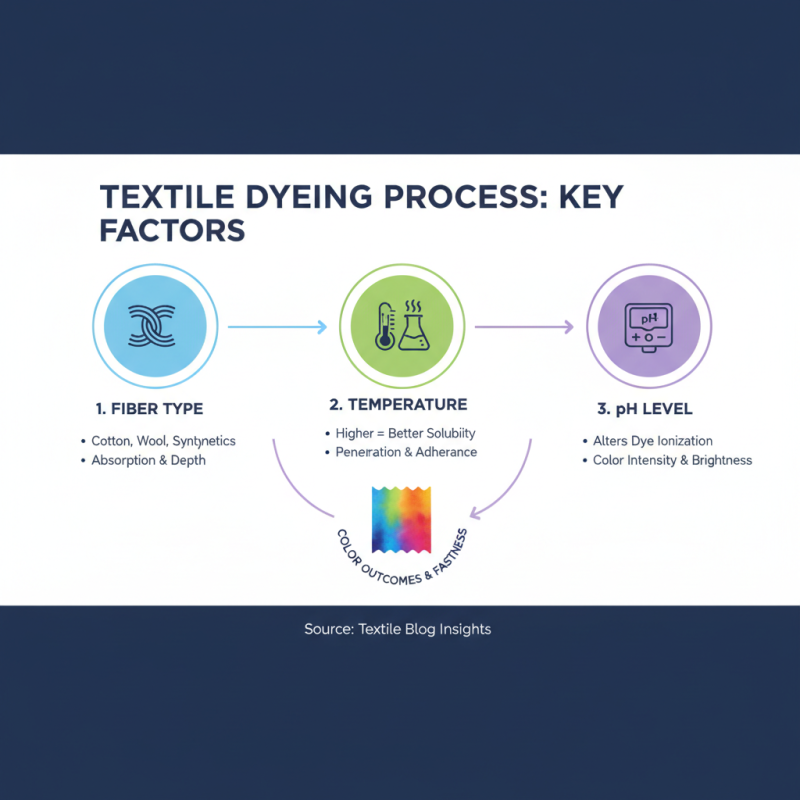
The dyeing process in textiles is influenced by various key factors that can significantly affect color outcomes and fastness. One of the primary considerations is the type of fiber being dyed. Different fibers, such as cotton, wool, and synthetic materials, vary in their chemical structure and affinity for dyes, which can lead to differing absorption rates and color depth. Additionally, the temperature and pH of the dye bath play critical roles in the dyeing process. Higher temperatures often increase the solubility of dyes, leading to better penetration and adherence to the fibers, while the pH levels can alter the ionization of dye molecules, impacting the final color intensity and brightness.
Another important factor is the dyeing method used, whether it’s batch, continuous, or digital printing. Each method presents unique advantages and challenges that can influence both the process efficiency and the resulting fabric quality. Furthermore, pre-treatment and post-treatment processes, including scouring and finishing, are vital for enhancing color fastness. Properly preparing the fabric before dyeing can remove impurities, ensuring an even dye application. Similarly, post-treatment processes, such as fixing agents or washing, can greatly enhance the durability of the color against factors like light exposure and washing, ensuring the longevity of the dyed textile. Understanding these factors is crucial for achieving high-quality, long-lasting colors in textile dyeing.
Common Techniques and Equipment Used in Textile Dyeing
The textile dyeing process is critical in determining the aesthetic appeal and commercial viability of garments. Employing various techniques and equipment is essential for achieving desired colorfastness and vibrancy. One of the most common techniques used is reactive dyeing, which involves the formation of covalent bonds between the dye and the textile, particularly effective for cotton fabrics. According to the "2021 Textile Dyeing Technology Report," the reactive dyeing market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2022 to 2026, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable and vibrant fabrics.
Another notable method is vat dyeing, particularly employed for dyeing fabrics like denim. This technique utilizes insoluble dyes that require a reduction process to make them soluble. The "Textile Industry Sustainability Report" highlights that vat dyeing accounts for approximately 15% of global dyeing processes, underscoring its importance. Equipment such as jet dyeing machines, known for their efficiency and reduced water consumption, are gaining traction within the industry. The same report notes that the adoption of advanced dyeing machinery can lead to up to a 30% reduction in water usage, which aligns with the industry's shift toward eco-friendly practices.
Top 10 Insights into the Textile Dyeing Process You Need to Know - Common Techniques and Equipment Used in Textile Dyeing
| Technique | Description | Equipment Used | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Dyeing | Dyeing method where fabrics are dyed in batches. | Dyeing machines, Dye baths | Cotton, Wool |
| Continuous Dyeing | Process where fabric is dyed continuously as it moves through machines. | Continuous dyeing ranges, Rollers | Large lengths of fabric |
| Disperse Dyeing | Dyeing method used for synthetic fibers. | Dyeing vats, Heat guns | Polyester fabrics |
| Reactive Dyeing | Chemical reaction between dye and fiber. | Reactive dyeing machines, Steamers | Cellulosic fibers |
| Azo Dyeing | Usage of azo dyes, which are synthetic dyes. | Dyeing vessels, Filters | Various textile materials |
| Natural Dyeing | Using natural materials from plants and minerals. | Dye pots, Stirring tools | Eco-friendly textiles |
| Direct Dyeing | Dyes applied directly onto fibers without any chemical reactions. | Dyeing machines, Batches | Wool, Silk |
| Heat Transfer Dyeing | Dyes transferred to fabric using heat. | Heat press machines, Transfer prints | Sportswear, Fashion apparel |
| Sublimation Dyeing | Dyes turn into gas and penetrate the fabric. | Sublimation printers, Heat presses | Polyester and blends |
Environmental Considerations and Innovations in Dyeing Processes
The textile dyeing process has significant environmental implications, prompting the industry to explore more sustainable methods. Traditional dyeing techniques often involve harmful chemicals and high water consumption, leading to pollution and resource depletion. To address these challenges, many companies are now focusing on eco-friendly alternatives that minimize environmental impact. Innovations such as natural dyes derived from plants, insects, and minerals are gaining popularity, offering biodegradable options that reduce chemical runoff into waterways.
Moreover, advancements in technology are playing a crucial role in transforming dyeing practices. Digital printing and automated dyeing machines significantly reduce water usage and energy consumption compared to conventional methods. These technologies enable precise color application, minimizing waste and enhancing efficiency. Additionally, efforts to recycle wastewater from dyeing processes are being implemented to mitigate pollution, further demonstrating the industry's commitment to sustainability. By adopting these innovative practices, the textile sector not only meets the growing demand for eco-conscious products but also contributes to a healthier planet.
Related Posts
-

Why is the Dyeing Process Essential in the Textile Industry for Quality and Sustainability
-

Best Spray for Textile Protection and Stain Resistance in 2023
-
2025 How to Master the Textile Finishing Process for Optimal Results
-
How to Achieve Sustainability in the Textile Industry: Key Strategies and Practices
-

2025 How to Master the Textile Finishing Process for Optimal Results
