How to Achieve Sustainability in the Textile Industry: Key Strategies and Practices
Sustainability in the textile industry has emerged as a critical focus in recent years, driven by the increasing environmental concerns and the urgent need for responsible production practices. According to a report by the Global Sustainability Textile Coalition, the textile industry is responsible for approximately 1.2 billion tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions annually, which is more than the combined emissions of all international flights and maritime shipping. This alarming statistic highlights the necessity for stakeholders across the industry to adopt sustainable practices that minimize ecological impact and promote resource efficiency.
Experts in the field are emphasizing the importance of sustainability in the textile industry. Dr. Maria Thompson, a leading researcher on sustainable fabrics, states, “To achieve true sustainability in the textile industry, we must prioritize innovative technologies and circular economy principles to reduce waste and improve overall textile life cycles.” This perspective emphasizes that concerted efforts towards sustainable sourcing, production, and recycling practices are essential for mitigating the environmental footprint of textile manufacturing.
As consumer awareness grows and regulatory measures tighten, the call for sustainability in the textile industry becomes even more urgent. Companies must not only focus on profit but also embrace ethical practices that ensure ecological balance and social responsibility. Therefore, exploring key strategies and practices in achieving sustainability in the textile industry is not just beneficial but imperative for a viable future.
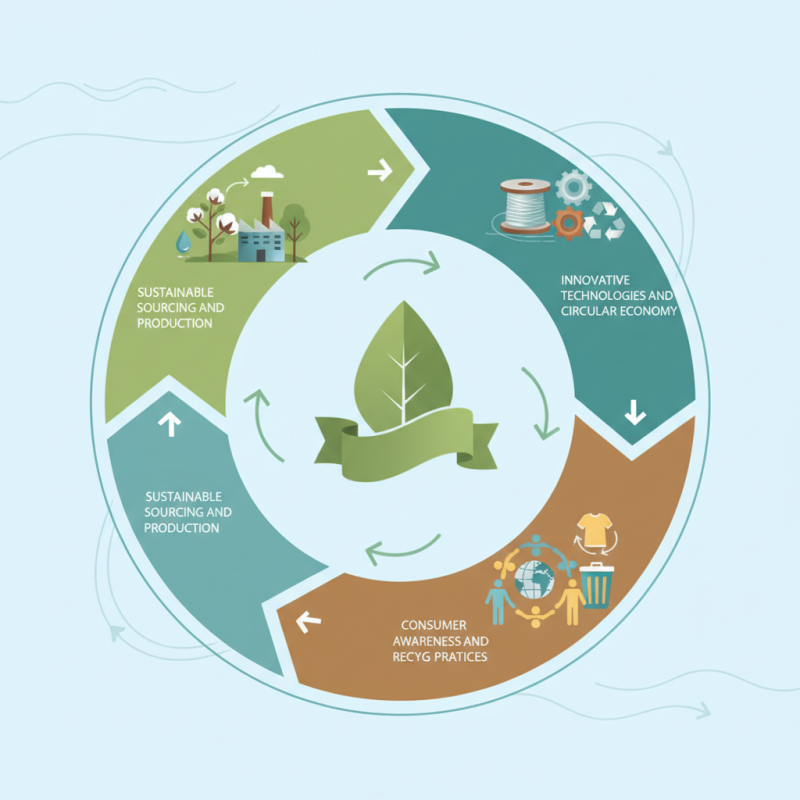
Understanding Sustainability in the Textile Industry

Sustainability in the textile industry has become an urgent necessity as the global population increases and environmental challenges escalate. According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, the fashion industry is responsible for approximately 10% of global carbon emissions, primarily stemming from manufacturing processes and the disposal of textiles. This alarming statistic highlights the critical need for sustainable practices within the sector to mitigate environmental impacts and promote long-term viability.
Understanding sustainability in the textile industry involves recognizing the life cycle of textiles, from raw material sourcing to production, distribution, and ultimately, consumer use and disposal. Reports from the Global Fashion Agenda indicate that adopting circular economy principles can potentially reduce the industry's carbon footprint significantly. For instance, transitioning to sustainably sourced materials and implementing efficient recycling systems could cut emissions by up to 44% by 2030. Emphasizing practices such as waste reduction, resource optimization, and ethical labor can create a robust framework for sustainable development, fostering innovation while addressing climate change and social equity within the industry.
Key Environmental Challenges Facing the Textile Sector
The textile industry faces a range of environmental challenges that threaten sustainability efforts. One of the most pressing issues is water consumption. The production process in textiles often requires significant amounts of water, leading to depletion of local water sources and pollution from dyeing and finishing processes. Furthermore, wastewater discharge containing harmful chemicals poses a risk not only to ecosystems but also to human health.
Another considerable challenge is the reliance on non-renewable resources and synthetic fibers, which contribute to carbon emissions and create an unsustainable waste problem. The fast fashion model exacerbates these issues by prioritizing quick production cycles and disposable garments, resulting in increased landfill waste. This cycle illustrates the urgent need for changes in production practices and consumer behavior.
**Tips:** One effective strategy for reducing the industry's impact is to embrace circular economy practices. This includes promoting recycling and upcycling of materials, empowering consumers to choose sustainable options. Additionally, manufacturers can invest in eco-friendly technologies that minimize water usage and waste throughout the production process. Adopting sustainable sourcing of raw materials can significantly mitigate the environmental footprint, steering the industry towards a healthier, more sustainable future.
How to Achieve Sustainability in the Textile Industry: Key Strategies and Practices
| Challenge | Description | Key Strategy | Example Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Pollution | Effluents from dyeing and finishing processes contaminate water sources. | Implement Closed-Loop Water Systems | Reuse treated wastewater for dyeing processes. |
| Waste Management | Textiles generate significant landfill waste. | Adopt Circular Economy Principles | Design for disassembly and recycling. |
| Carbon Footprint | High energy consumption in manufacturing processes. | Incorporate Renewable Energy Sources | Utilize solar panels for factory energy needs. |
| Resource Depletion | Overuse of non-renewable resources like petroleum in synthetic fibers. | Develop Bio-Based Materials | Research and implement organic cotton and other sustainable fibers. |
| Labor Practices | Unsafe working conditions in many textile factories. | Ensure Ethical Labor Standards | Regular audits of working conditions and fair wage policies. |
Sustainable Materials: Innovations and Alternatives in Textiles
The quest for sustainability in the textile industry has brought about a surge in innovative materials that seek to reduce the environmental footprint of textile production. One of the most promising alternatives is the use of organic fibers. These materials, such as organic cotton, linen, and hemp, allow for a reduction in harmful pesticides and fertilizers, promoting healthier ecosystems. Additionally, advances in technology have facilitated the development of synthetic fibers made from recycled plastic, diverting waste from landfills and oceans while creating durable fabrics suitable for various applications.
Moreover, the rise of bio-fabricated textiles, including those produced from fungi, algae, or agricultural waste, represents a transformative shift in the industry. These materials not only minimize reliance on petroleum-based fibers but also offer biodegradable options that can significantly lower the long-term environmental impact. Innovations such as these, combined with the increasing awareness among consumers, are helping to drive a more sustainable approach across the textile sector. By embracing these sustainable materials, the industry can move toward a greener future while still meeting the demands for creativity and functionality in textile design.
Implementing Circular Economy Practices in Textile Production
The implementation of circular economy practices in textile production is essential for fostering sustainability within the industry. This approach shifts the focus from a linear model of "take, make, dispose" to one that emphasizes regeneration and resource efficiency. By rethinking the entire lifecycle of textiles, companies can significantly reduce waste and minimize their environmental impact. This involves designing products with longevity in mind, utilizing durable materials, and promoting repair and recycling over disposal.
One of the critical strategies for implementing circular economy practices is material recovery and recycling. Textile manufacturers can adopt processes to reclaim fibers from discarded garments and reintroduce them into production. Developing technologies for recycling synthetic materials and enhancing the biodegradability of natural fibers are vital steps toward closing the loop. Additionally, brands can collaborate with organizations that specialize in textile recycling, creating a system where end-of-life products are seamlessly reintegrated into the production cycle. By prioritizing these practices, the textile industry can move towards a more sustainable future that respects both the environment and the economy.
Textile Industry Sustainability Practices
Strategies for Ethical Labor and Fair Trade in Textile Manufacturing
Ethical labor practices and fair trade are critical components in achieving sustainability within the textile industry. To cultivate a more equitable environment, manufacturers must ensure that workers are compensated fairly and treated with respect. This involves implementing transparent wage structures and providing safe workplace conditions. By engaging directly with workers and involving them in decision-making processes, brands can foster a culture of accountability and trust, which ultimately leads to improved job satisfaction and retention.
Moreover, embracing fair trade principles not only supports workers’ rights but also enhances brand integrity in the market. Fair trade certifications serve as a powerful tool to differentiate products, motivating companies to adhere to ethical guidelines. The promotion of small-scale producers and cooperative models in the supply chain ensures that profits are fairly distributed, empowering communities. As consumers increasingly demand ethical products, prioritizing fair labor practices is not only a moral obligation but also a strategic advantage for companies aiming for long-term success in a competitive market.


